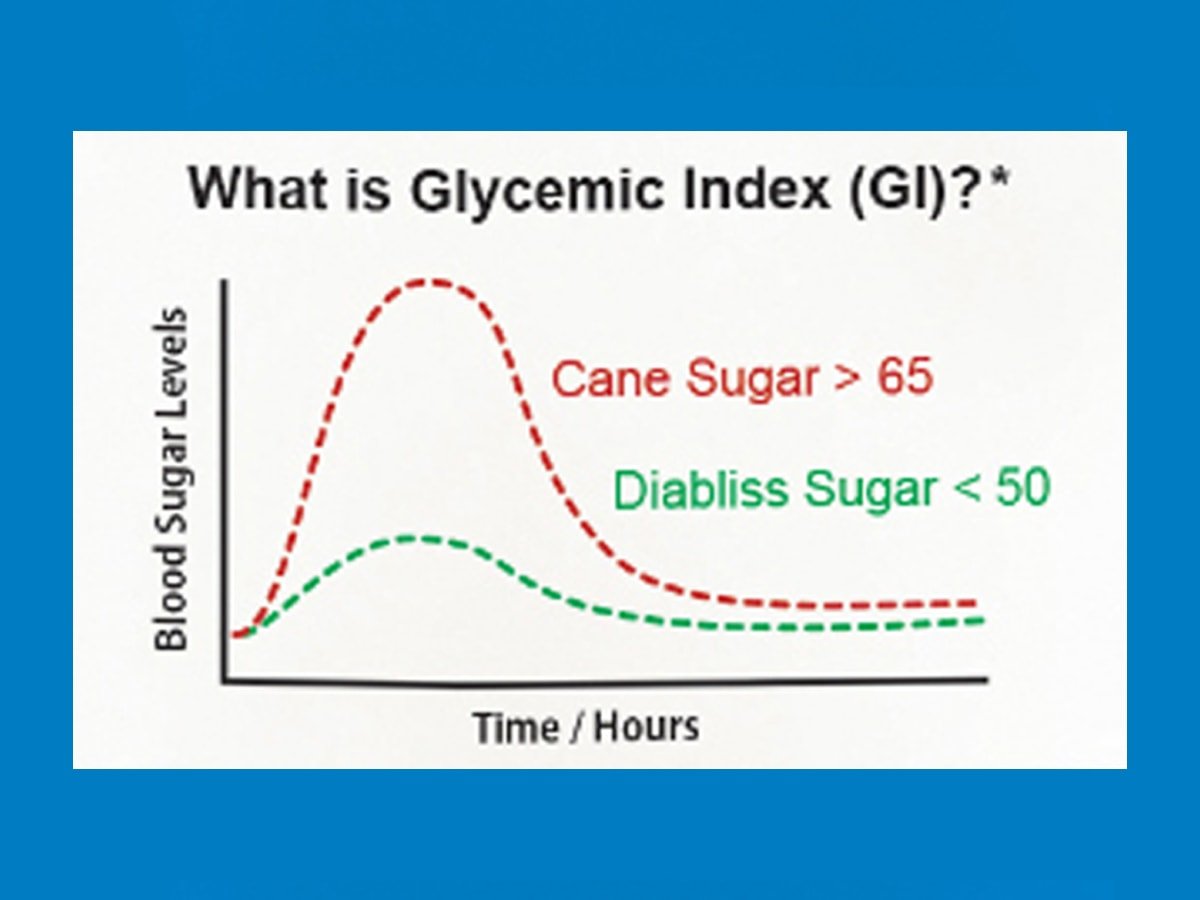
The Glycemic Index (GI) is a numerical scale used to rank carbohydrates based on their effect on blood sugar levels. It assesses how quickly a carbohydrate-containing food increases blood glucose compared to a reference food, typically glucose or white bread. The calculation involves comparing the blood sugar response to a standard amount of the test food with the response to the reference food.
The process for calculating the Glycemic Index is as follows:
- Selection of Test Subjects:
- Healthy individuals are chosen for the study.
- Baseline fasting blood glucose levels are measured for participants.
- Reference Food Consumption:
- Participants consume a measured quantity of the reference food, a substance known to elevate blood sugar rapidly.
- Blood Glucose Measurements:
- Blood glucose levels are measured at various intervals after consuming the reference food.
- The resulting response curve illustrates the speed at which blood sugar rises and falls.
- Test Food Consumption:
- Participants then ingest a measured amount of the test food containing the specific carbohydrate being studied.
- Blood Glucose Measurements for Test Food:
- Blood glucose levels are measured at the same intervals as after consuming the reference food.
- Calculation of Glycemic Index:
- The Glycemic Index is determined by comparing the area under the blood glucose response curve for the test food with that for the reference food.
- The formula typically used is: GI = (Area under the curve for test food / Area under the curve for reference food) x 100.
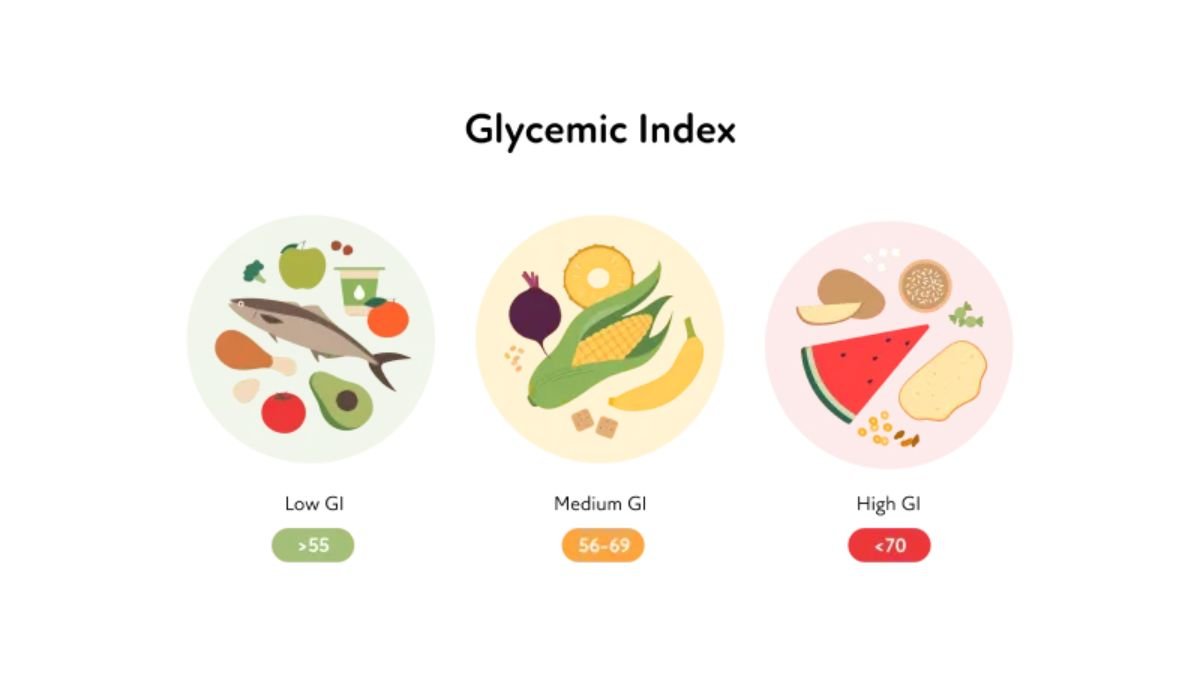
- Classification of GI:
- Foods are then categorized based on their Glycemic Index value:
- Low GI (55 or less)
- Medium GI (56-69)
- High GI (70 or more)
- Foods are then categorized based on their Glycemic Index value:
It’s essential to recognize that while the Glycemic Index is a valuable metric, other factors such as the Glycemic Load (GL), which considers both the quality and quantity of carbohydrates, may offer a more comprehensive understanding of a food’s impact on blood sugar.