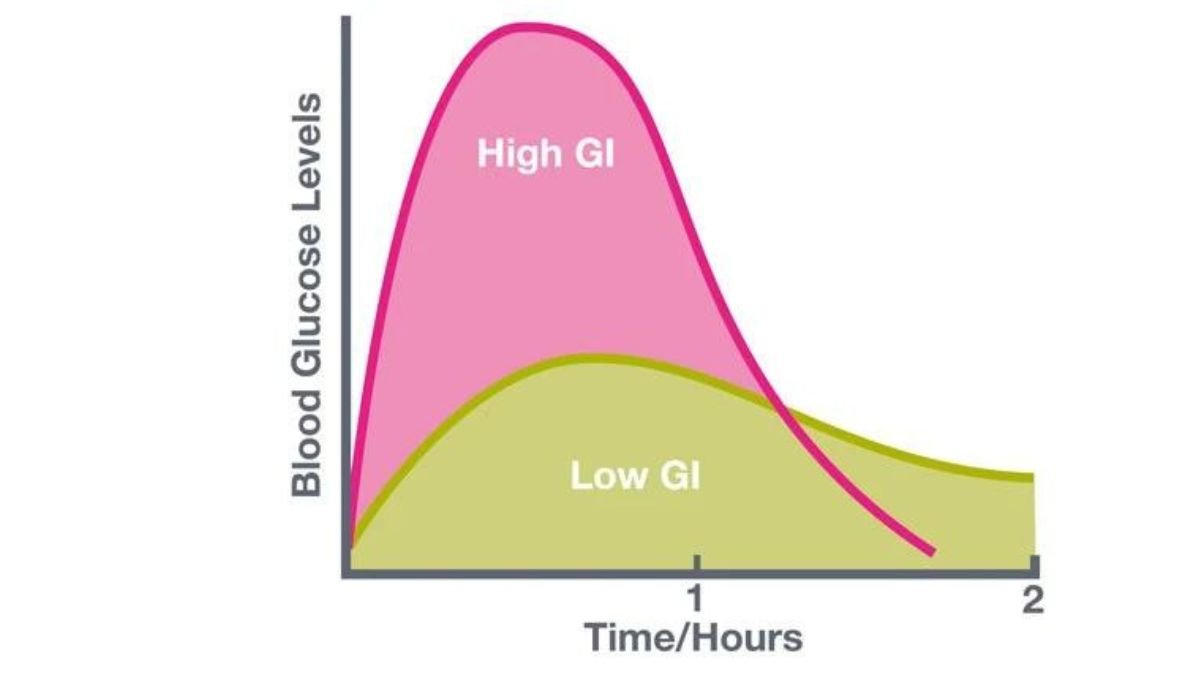
Glycemic response refers to the effect that consuming carbohydrates from food has on blood sugar levels. After carbohydrates are consumed, the body breaks them down into glucose, which enters the bloodstream, causing blood sugar levels to rise. The rate and extent of this increase in blood sugar levels varies depending on the type and amount of carbohydrate consumed as well as other factors.
The glycemic index (GI) is a scale that measures how quickly various carbohydrate-containing foods can raise blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI cause a rapid increase in blood glucose, while foods with a low GI cause a slower, more gradual increase in blood glucose levels.
Factors influencing glycemic response include:
- Type of carbohydrate: Simple carbohydrates, such as those found in refined sugars and processed foods, typically have a high GI, causing a rapid rise in blood sugar. Complex carbohydrates, found in whole grains, legumes and some fruits and vegetables, have a low GI because of their slow digestion.
- Fiber content: Foods high in fiber generally have a low glycemic response because fiber slows the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, leading to a slower rise in blood sugar levels.
- Processing and cooking methods: Processing and cooking methods can affect the glycemic response of foods. For example, cooking pasta al dente or consuming whole fruits instead of fruit juice may reduce glycemic response.
- Food combinations: Combining carbohydrates with protein, fat, or fiber-rich foods can slow digestion and absorption, reducing the overall glycemic response to the food.
- Individual factors: Individual responses to carbohydrates may vary. Factors such as genetics, insulin sensitivity, physical activity levels and overall health can affect how the body reacts to different foods.
Managing glycemic response is important for individuals with diabetes or those wishing to control blood sugar levels. Choosing low-GI foods and combining them with other macronutrients to create a balanced diet can help stabilize blood sugar levels and promote overall health.
Understanding the glycemic response of foods can help make informed dietary choices, especially for individuals who want to control blood sugar levels or maintain a steady energy supply throughout the day. When planning meals, it is important to consider a variety of factors beyond just GI, focusing on overall diet quality, portion sizes, and individual health needs.
Chat Now Gehuwala- Click Here
Glycemic response FAQ
1. What is glycemic response?
Glycemic response refers to the effect that food has on blood sugar levels following the consumption of carbohydrates. This involves the rise and fall of blood sugar levels in response to ingested carbohydrates.
2. What is the Glycemic Index (GI)?
The glycemic index is a scale that ranks carbohydrates in foods based on how quickly they raise blood sugar levels. Foods are classified as high, medium or low GI. High-GI foods cause a rapid rise in blood sugar, while low-GI foods cause a slower, more gradual rise.
3. How does glycemic response affect health?
High glycemic responses can lead to a rapid rise and subsequent drop in blood sugar levels, potentially contributing to increased appetite, lack of energy and a higher risk of type 2 diabetes, obesity and cardiovascular problems. Reducing the glycemic response to food can help manage blood sugar levels and reduce these health risks.
4. Which factors influence glycemic response?
Factors that influence glycemic response include type of carbohydrate (simple vs. complex), fiber content, food processing, cooking methods, food pairing, individual metabolism, genetics, insulin sensitivity, and overall food composition.
5. Are all high-GI foods unhealthy?
not necessarily. Some high-GI foods can provide quick energy and may be beneficial in specific situations, such as for athletes who need rapid energy replenishment after intense exercise. However, relying solely on high-GI foods without considering nutritional content may not be ideal for overall health.
6. How can I lower the glycemic response of meals?
To reduce glycemic response, focus on including low-GI foods such as whole grains, legumes, vegetables and fruits with low sugar content. Combine carbohydrates with foods containing protein, healthy fats and fiber to slow digestion and absorption.
7. Is glycemic response the only factor to consider for a healthy diet?
No, glycemic response is just one aspect of a healthy diet. Other factors such as overall diet quality, portion size, nutrient content, individual health conditions and lifestyle factors also play an important role in achieving optimal health.
8. How can glycemic response impact people with diabetes?
For individuals with diabetes, managing glycemic response is important to control blood sugar levels. Choosing low GI foods and monitoring carbohydrate intake can help maintain stable blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Understanding the glycemic response can help make informed dietary choices that contribute to stable blood sugar levels, sustained energy, and overall well-being. Consulting a health care professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance on managing glycemic response for specific health needs.