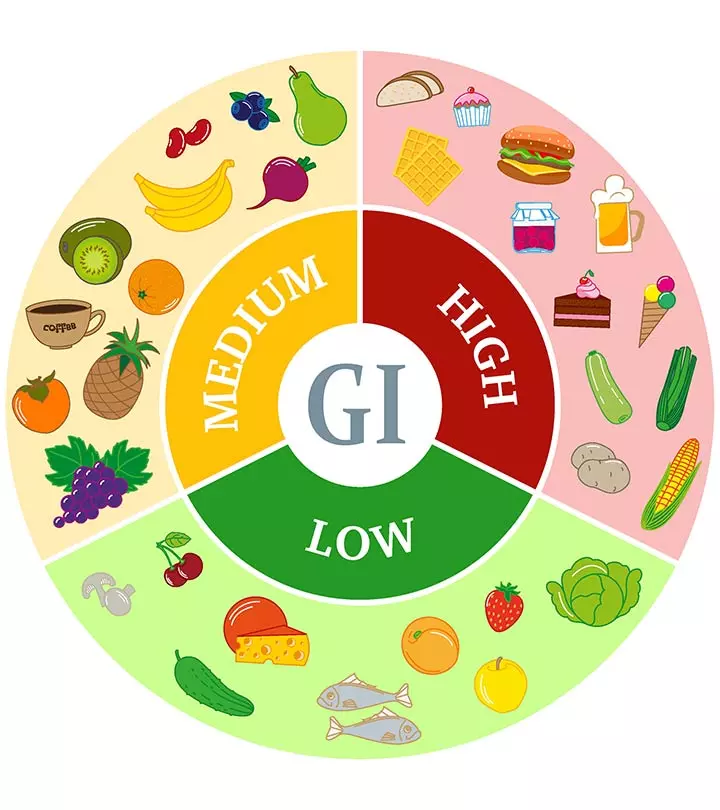
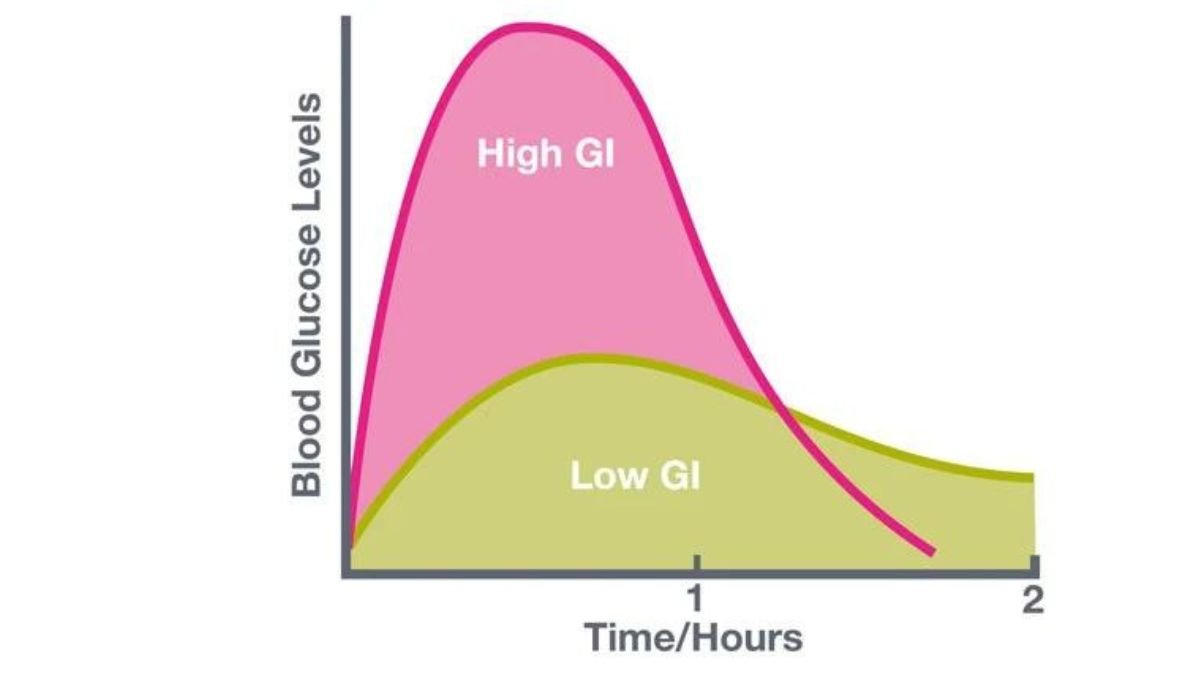
The Glycemic Index (GI) is a metric that measures how quickly carbohydrates in food raise blood sugar levels. Below is a list of foods categorized based on their estimated Glycemic Index levels. It’s important to note that actual GI values can be influenced by factors such as ripeness, cooking methods, and food combinations:
Low GI Foods (55 or less):
- Legumes (e.g., lentils, chickpeas, kidney beans)
- Non-starchy vegetables (e.g., broccoli, cauliflower, spinach)
- Whole grains (e.g., barley, quinoa, bulgur, oats)
- Sweet potatoes
- Most fruits (e.g., cherries, apples, pears, berries)
Medium GI Foods (56-69):
- Whole wheat products (e.g., whole wheat bread, whole wheat pasta)
- Basmati rice
- Couscous
- Oat bran
- Brown rice
High GI Foods (70 or more):
- White bread
- White rice
- Cornflakes
- Instant oatmeal
- Russet potatoes
It’s essential to consider the Glycemic Load (GL), which factors in both the quality and quantity of carbohydrates in a serving. The impact on blood sugar levels can also be influenced by the combination of foods in a meal and individual responses to different foods. For personalized dietary guidance or if you have specific health concerns, consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian is recommended.