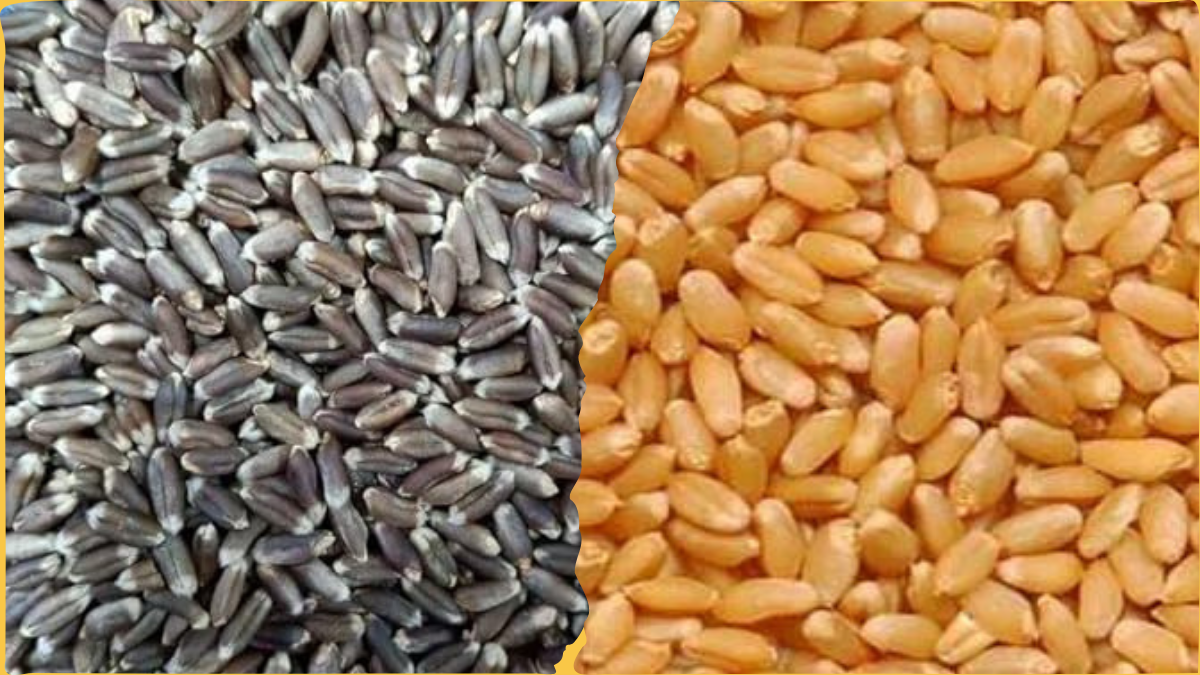
Black wheat and common wheat, commonly known as white wheat, exhibit distinct differences in appearance, nutritional composition, culinary applications, and potential health benefits.
- Color and Appearance of black wheat and normal wheat:
- Black wheat stands out because of its dark, almost black, or dark purple grains, which create an attractive visual contrast compared to the lighter-colored grains of white wheat.
- Nutritional Composition of black wheat and normal wheat:
- Black wheat typically contains high levels of anthocyanins, natural antioxidants responsible for its dark color. These antioxidants are associated with potential health benefits, such as reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. In contrast, white wheat often undergoes refining processes that remove some of the outer layers, potentially reducing its nutrient content compared to black wheat.
- Culinary Uses of black wheat and normal wheat:
- White wheat is widely used in baking because of its neutral flavor and fine texture. It is a common ingredient in various breads, pastries, and cake recipes, providing a light and soft texture to baked goods.
- In contrast, black wheat offers a more nutty flavor, adding depth and richness to dishes. It can be used in specialty breads, pasta, or desserts, providing a unique flavor experience and potentially higher nutritional value than white wheat.
- Health Benefits of black wheat and normal wheat:
- The high antioxidant content of black wheat, particularly anthocyanins, suggests potential health benefits by combating oxidative stress and inflammation, potentially contributing to overall well-being.
- White wheat, although preferred for its mild flavor and texture in culinary applications, may have lower nutrient levels due to the refining process, potentially resulting in less antioxidants and fiber than unrefined varieties.
- Availability and Usage of black wheat and normal wheat:
- White wheat is more prevalent and widely used in the food industry due to its familiarity and versatility in various culinary applications.
- Black wheat, although less common, is gaining attention due to its potential health benefits and distinctive flavor profile, leading to increasing interest in using it in specialty recipes and health-focused products.
In short, black wheat’s darker appearance and potentially higher antioxidant content distinguish it from white wheat, which is more refined and may have a milder flavor but potentially contains fewer nutrients. Both types of wheat offer unique characteristics, allowing for diverse culinary experiences and potential health benefits when included in a balanced diet.
Differences between black wheat and normal wheat FAQ
Q: What is the primary difference between black wheat and common wheat?
Answer: The primary difference is in their appearance and nutritional content. As the name suggests, black wheat has dark, almost black or dark purple grains, while common wheat, often called white wheat, has lighter colored grains. Nutritionally, black wheat has higher levels of antioxidants like anthocyanins than white wheat.
Q: What gives black wheat its dark color?
Answer: The dark color of black wheat is due to the presence of anthocyanins, natural antioxidants that are also found in blueberries and other dark-colored fruits and vegetables.
Q: How do black wheat and normal wheat difference nutritionally?
Answer: Black wheat contains high levels of antioxidants, particularly anthocyanins, which have potential health benefits such as reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. White wheat, which is often refined, may have lower levels of some nutrients due to the removal of the outer layers during processing.
Q: What are the culinary differences between black wheat and normal wheat?
Answer: White wheat is commonly used in baking because of its neutral flavor and fine texture, which is good for breads, pastries and cakes. Black wheat offers a nutty flavor profile and can be used in specialty breads, pastas, or desserts, adding depth and richness to dishes.
Q: Are there any health benefits associated with black wheat over normal wheat?
Answer: Black wheat’s high antioxidant content, particularly anthocyanins, suggests potential health benefits, such as reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. However, the overall effect on health may vary depending on individual dietary needs and consumption patterns.
Q: Can both types of wheat be incorporated into a balanced diet?
Answer: Yes, both black wheat and white wheat can be part of a balanced diet. They provide diverse culinary options and can contribute to overall nutritional intake when included in a variety of forms, taking into account individual dietary preferences and needs.
Q: How does the taste of black wheat differ from normal wheat?
Answer: Black wheat often has a nutty and slightly earthy flavor compared to the mild flavor of normal wheat. The distinctive flavor of black wheat can add depth and complexity to dishes.
Q: Can black wheat be used interchangeably with normal wheat in recipes?
Answer: Black wheat can be used in a variety of dishes, but its unique flavor and dark color can alter the taste and appearance of the final dish. Substituting black wheat for white wheat in recipes may require adjustments to accommodate its different characteristics.
Q: Are there specific culinary uses where black wheat shines compared to normal wheat?
Answer: Black wheat’s nutty flavor and high antioxidant content make it suitable for specialty breads, pastas, traditional dishes and desserts, where its unique flavor and potential health benefits can be appreciated.
Q: Does the nutritional difference between black wheat and normal wheat affect their dietary fiber content?
Answer: Both black wheat and common wheat contain dietary fiber, but the refining process applied to white wheat may result in slightly lower fiber content than unrefined black wheat.
Q: Are there any potential downsides to consuming black wheat compared to normal wheat?
Answer: While black wheat provides high antioxidant levels, it may not be as readily available as white wheat, which is commonly found in stores. Additionally, individual taste preferences may vary, and some people may not like the nutty flavor of black wheat in certain dishes.
Q: Can black wheat be considered a gluten-free alternative to normal wheat?
Answer: No, both black wheat and common wheat contain gluten, making them unsuitable for individuals with gluten sensitivity or celiac disease. For gluten-free options, other grains such as rice, quinoa or buckwheat are recommended.
Q: Is there a difference in the cooking or baking process between black wheat and normal wheat?
Answer: Black wheat can generally be used in cooking and baking just like normal wheat. However, due to its dark color and distinctive flavor, recipes may require some adjustment to balance the flavor and achieve the desired texture.
Q: Can black wheat and normal wheat be mixed together in recipes for a different flavor or nutritional profile?
Answer: Mixing black wheat and common wheat in recipes can result in a unique flavor profile and potentially their nutritional benefits. Experimenting with different proportions can provide varied culinary experiences.
Q: Are there any specific regions where black wheat is more commonly grown or consumed compared to normal wheat?
Answer: Black wheat may be more region-specific and less commonly cultivated than common wheat varieties. It may be found in some areas known for specialty or heritage grains rather than those grown on a large scale.
Q: How does the price of black wheat compare to normal wheat?
Answer: Black wheat price may vary depending on factors such as availability, demand and farming methods. In some cases, due to its specific nature, black wheat may be more expensive than commonly available white wheat.
Q: Can black wheat and normal wheat be milled into flour for baking purposes?
Answer: Yes, both black wheat and normal wheat can be ground into flour. Black wheat flour can impart a darker color and different flavor to baked goods than lighter-colored flour made from common wheat.
Q: Are there ongoing studies or research exploring the potential health benefits of black wheat compared to normal wheat?
Answer: Research is ongoing on the nutritional and health benefits of different varieties of wheat, including black wheat. Scientists continue to investigate the potential benefits and applications of different types of wheat in promoting health and well-being.